A Decade of Advances in Black Soldier Fly Research

Introduction
Over the past ten years, the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) has emerged as one of the most intensively studied and industrially exploited insect species. Its larvae are increasingly utilized in applications spanning animal feed, human food, and technical products such as biodiesel and bioplastics. The growing interest in black soldier fly research has led to significant advances across multiple scientific domains, including genetics, microbiology, nutrition, sustainability, and applied technologies.
Growth, Cultivation, and Nutritional Value of BSF Larvae
BSF larvae are highly versatile and can thrive on a wide range of organic substrates, including food waste, agricultural residues, and other biowaste streams. The composition of these substrates—especially their protein and carbohydrate content—plays a crucial role in determining larval growth rates, nutrient assimilation efficiency, and overall biomass yield (Eggink et al., 2022). Optimizing feed formulations has proven essential for maximizing productivity and economic viability in large-scale rearing systems.
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, photoperiod, and oviposition environments also significantly influence the reproductive success and developmental cycle of BSF populations (Julita et al., 2020). Understanding and controlling these variables are key to ensuring consistent and efficient colony maintenance.
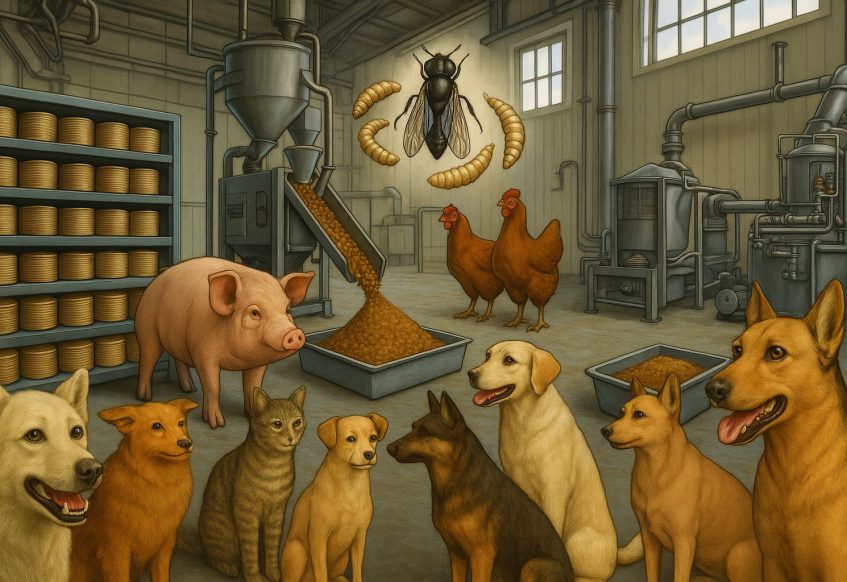
Applications in Animal Feed
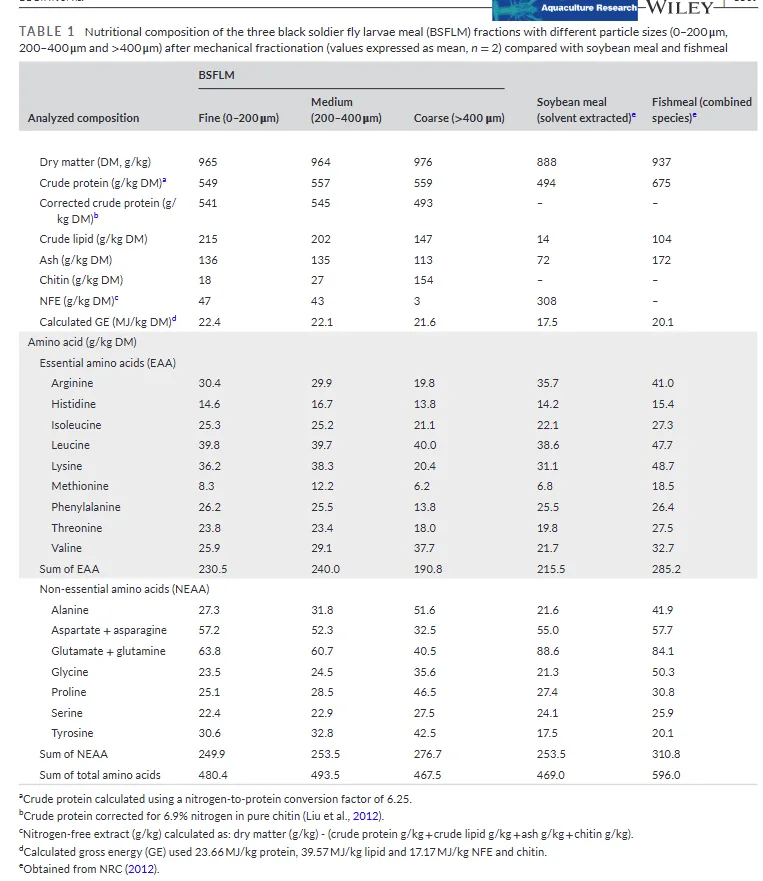
BSF larvae meal has rapidly gained recognition as a sustainable and nutrient-rich alternative protein source for livestock and aquaculture. It provides multiple benefits, including improved feed conversion ratios, enhanced gut health, and favourable effects on animal growth performance. Nevertheless, challenges remain regarding the high chitin content and the need for precise nutrient balancing to match species-specific dietary requirements (Eggink et al., 2022).
In aquaculture, BSF meal shows promising results, often displaying comparable digestibility and amino acid profiles to traditional fishmeal. However, inconsistencies in outcomes across different trials suggest that standardized rearing and processing protocols are needed to ensure product uniformity and quality.
Emerging Uses in Human Food
Although traditionally used in animal feed, BSF larvae are now gaining attention as a novel food ingredient for human consumption. Research into their incorporation into baked goods, pasta, snack bars, and protein supplements is expanding. BSF-derived lipids also present potential as alternative fats in processed foods, if deodorization techniques are employed to neutralize their distinct aroma and taste (Siddiqui et al., 2024). As consumer acceptance grows and regulatory frameworks evolve, BSF may play a significant role in the future of sustainable human nutrition.

Genetic Advances and Selective Breeding
Recent progress in the genetic characterization of Hermetia illucens has opened new avenues for selective breeding. The sequencing of both mitochondrial and nuclear genomes has revealed significant genetic variation, population structure, and adaptation mechanisms. These insights are critical for breeding programs aimed at enhancing desirable traits such as larval growth rate, waste conversion efficiency, disease resistance, and thermal tolerance (Facchini et al., 2022).
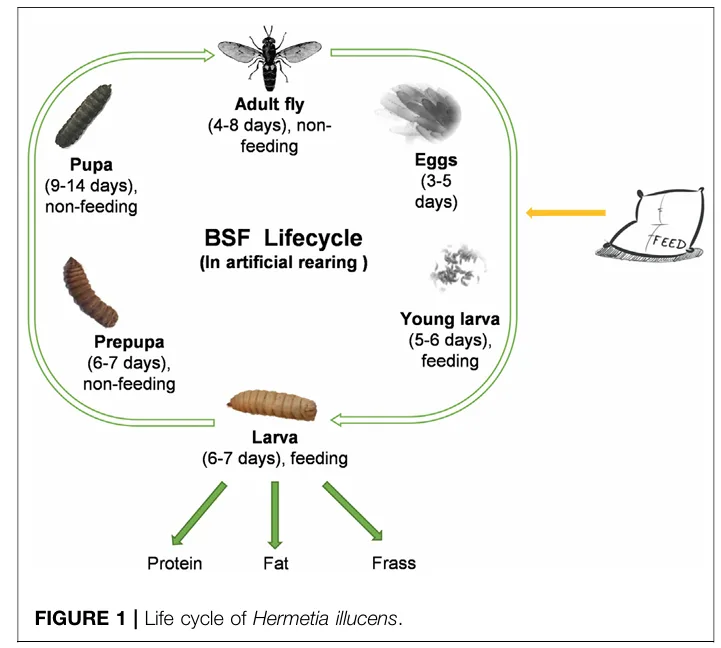
The Role of Gut Microbiota
BSF larvae possess a unique and functionally diverse gut microbiota that contributes significantly to their ability to digest complex organic matter. The microbiome plays a pivotal role in nutrient absorption, immune response, and overall larval performance. Understanding and managing this microbial ecosystem—through probiotics or substrate manipulation—has become an important strategy for improving the consistency and efficiency of BSF rearing systems (Silvaraju et al., 2024).
Sustainability and Future Outlook
BSF farming is widely regarded as a promising solution for addressing environmental and food security challenges. By converting organic waste into high-value products, BSF can contribute to circular economy models, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and alleviate pressure on conventional protein sources. However, further innovation is needed to overcome existing limitations related to large-scale production, biosecurity, and resource management (Odongo et al., 2024). Continued interdisciplinary research and policy support will be essential to fully unlock the potential of BSF in global sustainability initiatives.
For more information about:
- Insect Bioconversion of Waste, please contact us at the Insect school. https://www.insectschool.com/
- Turnkey Insect Farms – https://www.insectengineers.com/bsfturnkey/production
- If you would like to book BSF industry keynote speaker Bob Holtermans for your event – https://www.insectengineers.com/about-us/speaker-bobholtermans